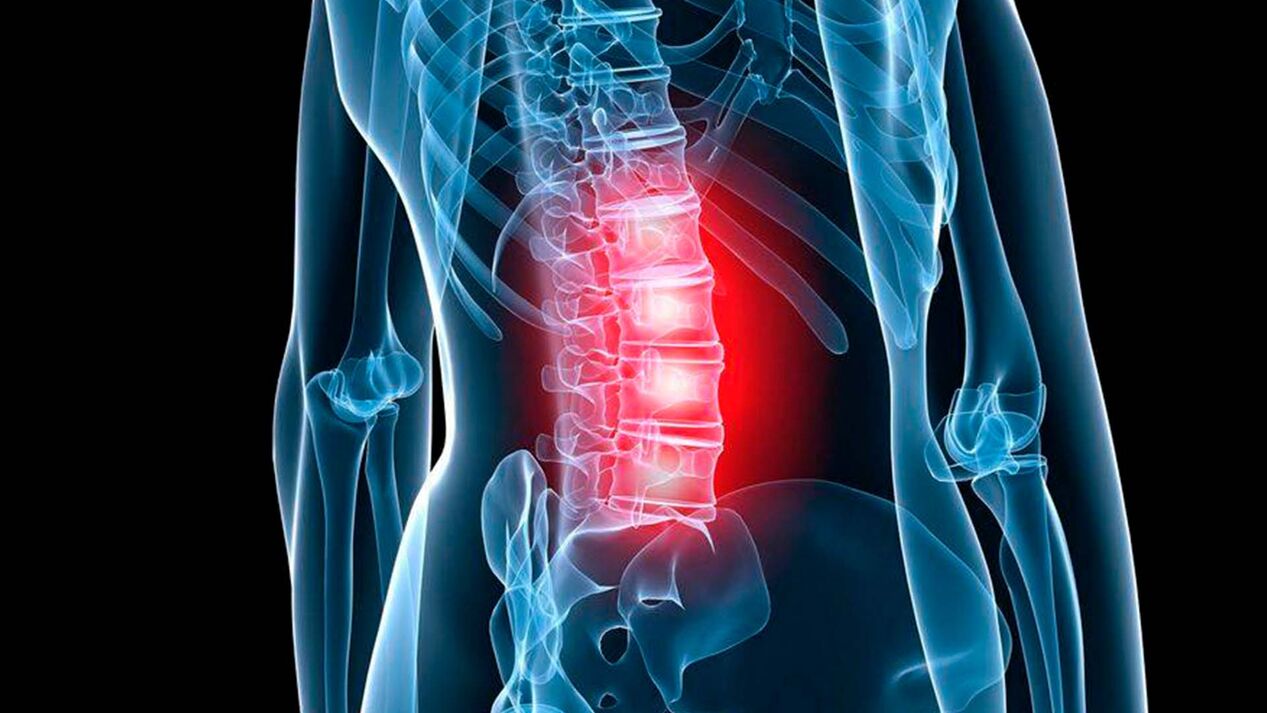
The lumbar spine is quite mobile and at the same time experiences heavy loads, regardless of the person's lifestyle and the work he performs. Therefore, osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is one of the most common cases of this disease. It affects both men and women, most often after 25-30 years, but recently the disease has become significantly younger. Osteochondrosis of the lower back, without treatment, progresses continuously and can even lead to disability.
Causes
Osteochondrosis is a degenerative disease, in which the intervertebral discs begin to collapse, there is a change in the distance between the vertebrae and the discs, displacement of the vertebrae relative to each other, followed by irritation or compression of the spinal cord, nerve endings and vessels blood vessels that run along the spine.
The reasons leading to the development of osteochondrosis, as a rule, are a consequence of excessive load on the spine: lifting weights, being overweight, back injuries, a sedentary lifestyle. The situation is significantly aggravated by diseases that lead to metabolic disorders, lack of sleep, stress and poor nutrition.
Symptoms
A common symptom of lumbar osteochondrosis is lower back pain. They can occur during physical activity, at rest, when changing posture, etc. Pain sensations can radiate, that is, spread beyond the place where the nerve is compressed, for example, radiate to the leg.
As the deformation of the vertebrae worsens, it becomes painful to perform even very simple movements: bending over, turning, etc. , which significantly worsens the quality of life. Symptoms of genitourinary disorders, including involuntary urination, may also appear.
Complications
Without timely and adequate treatment, progressive deformations of the intervertebral discs can lead to serious complications: the spine loses flexibility and, due to pain, it becomes impossible to perform simple actions such as bending and turning. With a long course of the disease, due to compression of the nerves by bone growths, complications extending to the genitourinary region and inflammation of the sciatic nerve are possible. Pain can occur even with coughing or minor physical activity.
Treatment
Medicines for osteochondrosis, as a rule, bring only temporary relief, relieving pain. Some of them warm up the muscles, locally increasing superficial blood circulation, but this is clearly not enough for the complete restoration of cartilaginous tissue. Especially if there is compression of nerves and blood vessels. Therefore, the symptoms of the disease usually reappear quickly.
Due to the development of the disease, not only the spine itself suffers, but also muscles, blood vessels and even internal organs. The work of an osteopathic doctor is not focused on treating the external symptoms of the disease, but on identifying and eliminating the root cause of its occurrence.
Osteopathic treatment has no contraindications for the treatment of osteochondrosis and is comfortable and safe for patients of any age. In 90% of cases it helps to avoid surgical treatment and, in addition, it is equally effective at any stage of the disease. Mainly with problems with internal organs, resulting from compression of the spinal cord and its roots. Furthermore, osteopathic treatment is necessarily indicated for patients with herniated discs and protrusions. It is completely safe and extremely effective. According to our observations, this is probably the most effective treatment method.
Lower back pain, numbness that spreads to the legs, feeling that the legs are literally falling off, inability to bend, turn and walk normally - these are the common symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
Lumbar osteochondrosis is a "disease of civilization" that is directly related to human upright posture. The disease causes stiffness of movement and back pain. These symptoms prevent you from leading an active lifestyle and can cause more serious illnesses, including internal organs. With osteochondrosis of the lower back, any sudden movement or lifting of weight can cause severe pain in the lower back.
No two patients are alike. Everyone is unique. In our practice, we have encountered diagnoses where the list of diseases read like a quote from a medical encyclopedia. For example, patient Anastasia, 69 years old: coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, stage II hypertension, chronic cholecystitis, left renal cyst, endometrial hyperplastic process. And, finally, osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, polyosteoarthrosis, osteoporosis. How can we help a patient like this? With so many serious neglected diseases? And what does lumbar osteochondrosis have to do with it?
The meaning of treatment, in the opinion of doctors in our centers, is to restore the speed and volume of blood flow in the systemic circulation by performing sequential exercises of the first, second and third floors of the body: that is, targeting the legs, abdomen and back.
In the absence of normal blood circulation in the lumbar spine, as well as the spinal column, a lack of oxygen occurs, which affects the normal functioning of the entire body, focusing on the internal organs of the small pelvis. Hence a lot of diseases, from internal organs to the cardiovascular system.
As a rule, when examining patients with lumbar osteochondrosis, we identify excessive tension in the paravertebral muscles of the thoracic and spinal regions, lack of elasticity in the muscles of the thigh and lower extremities in general - that is, muscle stiffness - are hard.
Most patients cannot reach the tips of their toes with their hands, and often even their knees. The muscles are so weakened that they cannot handle their own body weight well, much less perform simple household tasks.
Every day, the lumbar spine, as the most loaded part, is subjected to a series of static and dynamic loads, which is why it is rightly considered one of the most vulnerable. Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, the symptoms and treatment of which are discussed in this article, is a real "scourge" of patients after 35 years of age.
Lumbar osteochondrosisis a pathology characterized by the development of dystrophic disorders in the intervertebral discs of the lumbosacral spine. The discs provide flexibility and mobility to the spine, however, under the influence of a number of factors, their structure is disturbed, they lose firmness, elasticity, turgor, which can lead to the appearance of protrusion, and subsequently - a vertebral hernia, as well as compression of nerve endings and roots.
You can undergo treatment for lumbar osteochondrosis at the clinic. Timely seeking professional medical help is an opportunity to stop destructive processes and restore spinal health.
Causes
Lumbar osteochondrosis can appear due to several factors:
- Spine injuries; ;
- static and dynamic overloads of the spine;
- inadequate distribution of the load on the spine;
- spinal mobility;
- intense physical activity;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- age-related changes.
Clinical manifestations
The clinical manifestations of lumbar osteochondrosis in the initial stage are not clearly expressed in the form of limited mobility and stiffness. However, as the disease progresses, symptoms of pain appear, located in the lumbar region and back. The pain radiates to the sacrum, legs and (sometimes) the pelvic organs. The pain intensifies during bends and turns and often becomes unbearable. Additionally, the following symptoms are observed:
- limited movement;
- curvature, "tilt", scoliosis in the lumbar spine;
- muscle spasms;
- lameness in one or both legs;
- feeling of weakness, decreased sensitivity of the skin on the legs, decreased reflexes - with compression of nerve endings.
Diagnosis
Before prescribing treatment for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, specialists carry out comprehensive diagnostic studies that make it possible to make a correct diagnosis, determine the degree of development of the pathology and its consequences for both the spine and the patient's body as a whole. They include:
Osteochondrosis– one of the most common diseases of the 21st century.
A sedentary lifestyle, sedentary work, inadequate nutrition, constant stress - all these factors ultimately lead to wear and tear of the intervertebral cartilage.
The cartilage loses elasticity, becomes fragile and the disease progresses, significantly worsening the quality of life.
Patients with osteochondrosis experience problems of varying complexity: from pain to disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
The reasons for the development of osteochondrosis are also:
- Age-related changes
- Spine injuries
- Posture disorders
- Rachiocampsis
- Flat foot
- Hereditary predisposition
- Excessive exercise
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis are, in particular, pain in the back or lower back, aggravated by sudden movements and changes in body position, radiating to the buttocks and legs, anterior abdominal wall, groin area, accompanied by burning, tingling , numbness, and the appearance of "goosebumps".
In addition, with lumbar osteochondrosis, there is a decrease in skin sensitivity on the thighs, buttocks and legs, and less often on the feet. There is an increase in coldness in the legs, a feeling of weakness in the legs, as well as curvature of the lumbar spine.
You need to know that in most cases the cause of complaints about lower back pain is precisely osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine.
Patients with osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine require timely and adequate treatment. Otherwise, the destruction of cartilage, ligaments and vertebrae will progress, which can lead to dysfunction of internal organs and disability.
Modern restorative medicine can significantly improve the condition of patients with lumbar osteochondrosis. Significant improvements can be achieved through a range of methods, including physiotherapy, acupuncture, medication, massage therapy and much more, according to individual prescriptions.
Lumbar osteochondrosis- a very common form of osteochondrosis. It occurs in men and women. Patients themselves often mistakenly "diagnose" it as a "pinched lumbar nerve", since the pain that occurs in lumbar osteochondrosis is concentrated in the sacral region.
In general, pain is the main symptom of this disease. It comes in different intensities. Some people suffer from aching pains that occur after sitting or sleeping for a long time, others suffer from "shooting" and shooting pains. In this case, the pain occurs when the patient takes an uncomfortable position. Due to severe pain, the person is unable to straighten up.
Pain in the sacral regionoccur due to compressed nerve endings, muscle swelling, and compressed nerve roots. Pain may also begin due to irritation of the lumbar ligaments.
Pain in the lower backit intensifies with almost any movement of the body, especially when bending forward. Even a simple sneeze or cough causes increased pain.
However, lumbar osteochondrosis has other symptoms. First of all, these are disorders in the sensitivity of the skin, the muscles of the legs and the lower half of the body. Some patients also experience weakening of tendon reflexes in the legs and, in particularly severe cases, their complete disappearance. Osteochondrosis is a factor in the development of scoliosis of the lumbar spine, especially in children and the elderly.
Lumbar osteochondrosis also has the following clinical symptoms:
Lumbar osteochondrosis symptomand at the same time, its most unpleasant complication is spinal instability. The disc stops attaching the vertebra. As a result, when under load, the lumbar spine practically "slides" from the sacrum, which causes intense and unbearable pain. Also, with this pathology, the functioning of internal organs is disturbed. First of all, this concerns the genitourinary system. Lumbar osteochondrosis affects men's potency and causes gynecological problems in women.
Unfortunately, modern medicine has not yet invented a remedy that could quickly and easily solve this problem. The treatment of osteochondrosis is very complex and long-term. It must be comprehensive; Only in this case can good results be achieved.
Treatment measures for lumbar osteochondrosis include:
In particularly severe cases, surgical intervention may be performed.
INosteochondrosis treatmentSanatorium treatment is very effective.
In case of exacerbation of osteochondrosis, the patient is prescribed bed rest. Furthermore, the patient must lie down on a hard mattress.
In case of severe crises, the patient needs to move as little as possible and seek help from a specialist. A neurologist is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of osteochondrosis.
If any of the above symptoms are detected, you should consult a neurologist
You can make an appointment by calling 8 (928) 337-60-60.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar region
Of all diseases of the peripheral nervous system, osteochondrosis of the spine accounts for 80%, of which 60-80% affect the lumbar region, consisting of 5 vertebrae. In 40% of people, the first signs of the disease appear at the age of 30-35. In old age, spinal osteochondrosis is diagnosed in 90% of people. Painful sensations are experienced by 7 out of 10 people, exacerbation can last from 6 to 16 months.
Development stages
1st – appearance of degenerative diseases, affecting nerve endings and interrupting blood supply. The inflammatory process causes pain that radiates to the legs. The patient feels occasional tingling in the back and buttocks. Appears after great physical exertion.
2nd – the outer layer of the intervertebral disc (fibrous ring) is destroyed. The distance between the vertebrae decreases, the nerve endings are compressed, which causes strong and sharp pain. Symptoms are especially pronounced when walking.
3rd – due to excessive mobility of the vertebrae, muscle fibers and nerve endings become compressed. Spasms, numbness, burning pain, hernias occur - displacement of the intervertebral disc into the spinal cord.
4th – the growth of pathological exostoses in the bone structure. The column literally "turns to stone". Progressive osteoarthritis and lack of treatment immobilize the patient.
Reasons for development
The disease develops slowly, under the confluence of a number of circumstances, that is, the development of the disease depends on the influence of not one, but several factors:
Sedentary lifestyle (sedentary lifestyle), sedentary work, low level of physical activity. At first glance, they are not dangerous. However, with prolonged exposure, muscle tone, the so-called "muscle corset", becomes weakened. Supports the spine and internal organs. Thus, physical inactivity causes disruptions in the functioning of various systems - blood circulation, breathing, digestion.
Overweight. With a BMI (Quetelet body mass index) above 25 kg/m2, excess weight creates additional stress on the body: it puts pressure on the spine, overloads the joints and impairs blood supply.
Endocrine pathological processes. Hormonal imbalance, disturbances in the functioning of the adrenal glands and thyroid gland "slow down" the body's metabolism. Frequent hormonal changes "eliminate" calcium from bone tissue, making it weak and fragile.
Unbalanced diet. Popular and affordable fast food fully satisfies the body's energy needs, while from the point of view of saturating the body with the necessary vitamins and microelements, it is absolutely useless.
In men whose profession involves significant physical activity, lumbar osteochondrosis occurs much more often.
Symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
Pain is the main marker of the onset of the disease and its location. Based on the nature of the occurrence, frequency and duration, a preliminary diagnosis can be made. Most often, patients with lumbar osteochondrosis experience severe pain that radiates to the leg, groin area and coccyx. In a horizontal position, the discomfort disappears.
Spinal nerves extend from the trunk of the spine to different parts of the body. Each nerve is responsible for a specific area. This is called "segmental innervation. "It is for this reason that the affected nerve "responds" in a specific area: this is how "radicular syndrome" manifests itself.
The spinal nerve map allows you to identify pain in a specific area of the spine: C1-C8 - 8 cervical, T1-T12 - 12 thoracic, L1-L5 - 5 lumbar, S1-S5 - 5 sacral, C0 - 2 coccygeal. Signs of osteochondrosis depending on segmental innervation:
L3-L4 – weak knee reflex, partial numbness, episodic loss of sensation are noted along the anterior surface of the thigh;
L4-L5 – muscle weakness, the patient is unable to fix the body while standing on the heels, pain and sensory disturbances spread throughout the lumbar region to the buttock, as well as along the entire lateral surface of the thigh (from top to bottom).
L5–S1 – tremors in the calf muscle, inability to stand on tiptoe, pain in the back of the thigh.
In rare cases, the radicular arteries are also involved in the destructive process, provoking a stroke - a dangerous pathology in which the patient experiences paresis and paralysis and dysfunction of the pelvic organs.
Pain reflex symptoms
Lumbago or low back pain (in this case not sciatica! ) – sharp pain. Any strange movement, even sneezing and coughing, causes a spasm. The patient spontaneously changes the position of the body, moving it to the side. Attempting to assume an upright position causes new low back pain.
Lumbodynia is a dull, aching pain that occurs on one side. Periods of remission are followed by exacerbation, which gradually evolves into severe pain.
Lumboischialgia - painful sensations appear in the leg.
Side signs of the disease are not so typical and can easily be confused with symptoms of another problem: impaired sweating (hypohidrosis), pallor of the skin in the affected area due to poor blood circulation, severe dryness and peeling.
Diagnosis
In the initial phase, a complete medical history of the patient is collected. The general picture must be supplemented by the conclusions of a surgeon, orthopedist, neurologist and rheumatologist. Specialists subject the patient to a visual examination to assess changes in posture, muscle tone and skin sensitivity.
X-ray is performed for the primary diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis of the 1st degree, it is used to examine the condition of intervertebral discs, pathologies of the spinal cord, and also assess the general condition of the spine. However, this type of diagnosis does not provide complete information about the affected tissues.
Computed tomography (CT) is a highly sensitive exam that uses a beam of ionizing rays. Computed tomography records the degree of disc deformation, inflammatory processes in the spinal cord membrane and nerve endings in a layer-by-layer image.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) informatively shows the general condition of muscle mass, blood vessels and ligaments. Detects tumors and inflammatory processes.
Myelography is one of the ways to visually assess the condition of the spinal cord and nerve roots by injecting a contrast agent with a needle into the cavity between the pia mater and the spinal arachnoid, filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Similar to CT scan, MTP and X-ray, the procedure is performed in real time.
Neurological examination of sensitivity and reflexes for pathologies is a complex of studies that includes a screening method for studying the symmetry of the limbs, testing vibration sensitivity and assessing Babinsky, Chaddock and Oppenheiman reflexes.
Treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis
The effectiveness of conservative treatment is achieved through a combination of medications from several groups, massage and manual therapy. However, at stage 3, lumbar osteochondrosis can no longer be cured with conservative methods, surgical intervention is required. One of the methods of surgery for osteochondrosis is microdiscectomy. This is a neurosurgical operation to remove a hernia without damaging nerve structures. It is performed under general anesthesia. The patient can walk on the 3rd day.
Drug therapy (for stages 1-2)
- Analgesics for pain relief: local (ointments, gels), oral (tablets, suspensions), intramuscular (injectable solutions).
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to prevent the development of the inflammatory process. Reduces temperature, removes swelling. Most often, gels and tablets are used, in more severe cases (inflammation of the sciatic nerve) - injections. The Prima course lasts from 7 to 14 days.
- Muscle relaxants. Prescribed in the acute period of muscle spasms, as well as during the period of remission to consolidate the effect.
- Chondroprotectors. Blocks destructive processes in intervertebral discs, promotes regeneration, improves metabolism in cartilaginous tissues.
- Group B vitamin complexes. Improve nerve conduction.
- Diuretics. Reduces swelling.
As emergency aid at the time of exacerbation, powerful injections are used - paravertebral blockade, which causes temporary loss of sensitivity.
Prevention
- Active lifestyle combined with moderate physical activity;
- Choose comfortable or, if indicated, orthopedic footwear;
- Body weight control;
- Sleep only on an orthopedic mattress and pillow;
- Office furniture with flat backs only;
- Refusal of heavy loads on the back and spine. When carrying heavy items, the load must be evenly distributed between both hands.