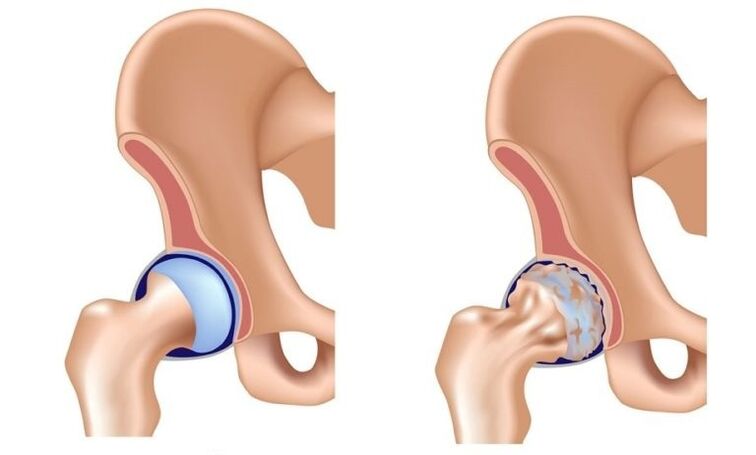
Hip joint arthrosis (deformation arthrosis, coxarthrosis, osteoarthritis) is a slowly progressive degenerative-degenerative disease, leading over time to destroy the pain of the affected and persistent joint and limiting mobility.
The disease affects people over 40, women get sick several times more than men.
In the general structure of arthrosis, arthrosis of the hip joint belongs to the main role.This is due to the widespread congenital pathology of the hip joints (dysplasia), as well as to significant physical effort, to which these joints are susceptible.
Risk factors and causes of hip joint arthrosis
In the pathological mechanism of the development of hip arthrosis, the lead role belongs to a change in the physical-chemical characteristics of synovial (intra-articular) fluid as a result of which it becomes denser and viscous.This worsens your lubricating qualities.When moving, the surfaces of the joint cartilage begin to rub each other, they become rough, covered with cracks.Small hyaline cartilage particles are abandoned and fall into the joint cavity, causing the development of aseptic (non -infectious) inflammation in it.As the disease advances in the inflammatory process, bone tissue is attracted to the inflammatory process, which leads to aseptic necrosis of femoral head sections and the acetabulum surface, osteophyte formation (bone growth), increased inflammation and causing severe pain during movement.
In the late extension of hip joint arthrosis, inflammation is also thrown into the surrounding tissue joint (blood vessels, nerves, ligaments, muscles), which leads to the appearance of signs of periartritis.As a result, the hip joint is completely destroyed, its functions are lost, the movement ceases in it.This condition is called ankylosis.
Causes of hip joint arthrosis:
- congenital lip of the thighs;
- hip dysplasia;
- aseptic necrosis of femoral head;
- Peters' disease;
- hip joint injuries;
- Infectious arthritis of hip joint;
- gonarthrosis (deformed osteoarthritis of knee joint);
- osteochondrosis;
- Overweight;
- professional sports;
- Smooth feet;
- Curvature of the spine;
- A sedentary lifestyle.
The pathology is not inherited, but the child inherits the characteristics of the musculoskeletal system's structure of his parents, which can cause arthrosis of the hip joint under these conditions.This explains the fact of the existence of families, whose incidence is greater than in the general population.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the etiology, hip arthrosis is divided into primary and secondary.Secondary arthrosis develops against the antecedents of other hip joint diseases or their injuries.The primary form is not related to the previous pathology, the reason for its development is usually not possible;In this case, they talk about idiopathic arthrosis.
COKSARTROSIS is one or bilateral.
Stages
Three stages (grade) are distinguished during hip joint arthrosis:
- Initial pathological changes are expressed slightly, provided that the timely and adequate treatment is reversible.
- Progressive Coxarthrosis - characterized by a gradual increase in symptoms (joint pain and impaired their mobility), changes in joint tissues are already irreversible, but therapy may decrease degenerative processes.
- The final movement in the joint is lost, ankylosis is formed.Treatment is only surgically (replacing artificial joint).
Endoprophetic operations in 95% of cases ensure a complete restoration of limb mobility, restore patient performance.
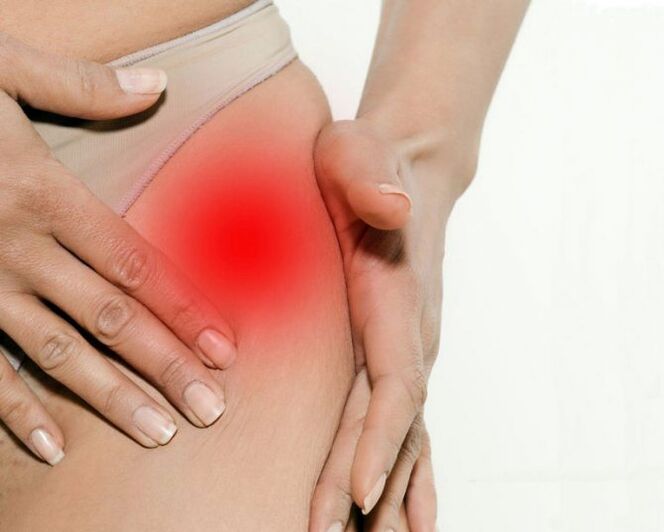
Hip Articulation Arthrosis symptoms
The main signs of hip joint arthrosis:
- Groin pain, hips and knee;
- a feeling of rigidity in the affected joint and the limitation of its mobility;
- Claudication;
- kidnapping restriction;
- Atrophic changes in the thigh muscles.
The presence of certain symptoms of hip joint arthrosis, as well as their severity, depend on the degree of disease.
In the 1st degree of arthrosis of the hip joint, patients complain about the pain in the affected joint that occur under the influence of physical activity (prolonged walk, running).In some cases, the pain is located in the knee or thigh area.After a short rest, the pain goes through its own.The volume of limb movements is completely preserved, the march is not broken.The following changes are observed on the radiography:
- Light unequal decrease in joint gap lumen;
- Osteophytes located on the inner edge of the turnaround.
Any changes in the neck and femoral head are not detected.
With the degree of arthrosis of the hip joint, the pain also appears at rest, including at night.After physical activity, the patient begins to bear, a characteristic gear is formed.The so -called initial pains appear - after a long period of immobility, the first steps cause pain and discomfort that pass and then return after a long load.In the affected joint, the volume of movements (abduction, internal rotation) is limited.Radiography shows that joint gap is unevenly reduced and its lumen is 50% of the standard.The osteophytes are located along the inner and outer edge of the joint cavity, going beyond the limits of the cartilage.Femoral head contours are uneven due to deformation.
With the degree of arthrosis of the pain articulation, intense and constant, not stopping at night.Walking is significantly difficult, the patient is forced to trust the cane.The volume of movements in the affected joint is markedly limited, then to completely interrupt.Due to the atrophy of the hip muscles, the pelvis deviates on the frontal plane and the limb is reduced.Trying to compensate for this shortening, patients when they walk are forced to reject the body toward the injury, which further increases the load in the painful joint.In radiographs, various bone growths, a significant narrowing of joint gap and a pronounced increase in the femur's head are detected.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of hip joint arthrosis is based on the data of the clinical image of the disease, the results of the medical examination and instrumental studies, among which the main value belongs to visualization methods - radiography, calculated or magnetic resonance.They allow not only to determine the presence of hip joint arthrosis and evaluate its degree, but also identify the possible cause of the disease (trauma, juvenile epiphysilysis, Peters disease).
The differential diagnosis of hip arthrosis with other diseases of the musculoskeletal system is quite complicated.In the degree of arthrosis II and III of the hip joint, muscle atrophy develops, which can cause intensive pain in the characteristic knee joint or gonarthrosis (knee joint diseases).For the differential diagnosis of these states, the palpation of the knee and hip joints is palpated, the volume of motion is determined and are also examined by radiologically.
In spine diseases, in some cases, the nerve roots of the spinal cord with the development of pain syndrome are squeezed.The pain can radiate to the hip joint area and mimic the clinical image of your defeat.However, the nature of pain with root syndrome is slightly different than with hip joint arthrosis:
- Pain occurs as a result of weight lifting or marked movement, not under the influence of physical effort;
- The pain is located in the gluteal region, not in the inguinal region.
With root syndrome, the patient can take the leg calmly to the side, while with hip joint arthrosis, the kidnapping is limited.A characteristic sign of root syndrome is a positive symptom of tension - the appearance of a marked pain while trying to raise the straight leg in the patient's back.
Hip articulation arthrosis affects people over 40, women get sick several times more than men.
Hip articulation arthrosis should also be differentiated with the loyal burrysto (puncture).Vable bursitis develops faster within a few weeks.Usually it is preceded by significant physical effort or injury.In this disease, the pain is much more pronounced than with arthrosis of the hip joint.At the same time, shortening the limb and limiting their mobility is not detected.
The clinical image of atypical reactive arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis can resemble the clinical manifestations of hip articulation arthrosis.However, pain occurs in patients mainly at night or at rest, when the walk does not intensify, but, on the contrary, weakens.In the morning, patients observe joint stiffness, which passes after a few hours.
Treatment of hip joint arthrosis
The orthopedic people are involved in the treatment of hip joint arthrosis.With grade I and II of the disease, conservative therapy is indicated.With pronounced pain syndrome, patients are prescribed non -esteroid anti -inflammatory drugs in a short course.They should not be accepted for a long time, as they are not only able to have a negative effect on the gastrointestinal tract organs, but also to suppress the regenerative skills of hyaline cartilage.
Under the hip articulation arthrosis treatment regime, they include chondroprotectors and vasodilators, which creates ideal opportunities to restore damaged cartilage tissues.With pronounced muscle spasm, it may require the appointment of central muscle relaxants.
In cases where it is not possible to stop pain syndrome with non -esteroid anti -inflammatory drugs, resort to intra -articular corticosteroid injections.
Local treatment of hip arthrosis using heating ointments allows to reduce muscle spasm and weaken the pain slightly due to distracted action.
In complex hip arthrosis therapy, physiotherapeutic methods are also used:
- Magnetotherapy;
- inductothermia;
- UHF;
- laser therapy;
- Ultrasound treatment;
- massage;
- Medical gymnastics;
- Manual therapy.
Food nutrition for hip joint arthrosis aims to correct body weight and normalization of metabolic processes.Reduction of body weight reduces the load in hip joints and thus decreases the progression of the disease.
To unload the affected joint, the doctor may recommend that patients go to crutches or sugarcane.
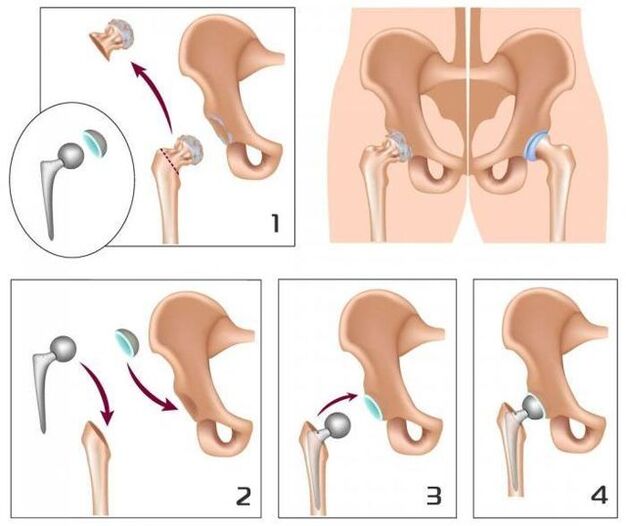
With the degree of arthrosis III of the hip joint, conservative treatment is inefficient.In this case, it is possible to improve the patient's condition, it is possible to return normal mobility only as a result of surgical intervention - replacing artificial joint (joint and articular endopriptetic).
Possible consequences and complications
The most severe complication of progressive arthrosis of hip joint is the deficiency due to loss of movement in the joint.With bilateral cOKSARROSIS, the patient loses his ability to move independently and needs constant strange care.A long stay in bed in a position creates the prerequisites for the occurrence of stagnant pneumonia (hypostatic), which is difficult to succumb and can lead to death.
The pathology is not inherited, but the child inherits the characteristics of the musculoskeletal system's structure of his parents, which can cause arthrosis of the hip joint.
Forecast
Arthrosis of the hip joints is a progressive chronic disease that can be completely healed in the early stages, subject to the elimination of the cause of the disease.In other cases, therapy allows you to slow down your course, however, over time, there is a need for implantation of hip endoProstheses.Such operations in 95% of cases provide a complete restoration of limb mobility, restore patient performance.The life of modern prostheses is 15 to 20 years, after which they are subject to replacement.
Prevention
The prevention of hip arthrosis aims to eliminate the causes that can lead to the development of this disease and includes:
- Detection and treatment timely diseases and hip joint injuries;
- rejection of a sedentary lifestyle, regular but not excessive physical activity;
- Body weight control;
- Rational Nutrition;
- Refusal of bad habits.